133. Clone Graph
Difficulty: Medium
Topics: Depth-first Search, Breadth-first Search, Graph
Similar Questions:
Problem:
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph, return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
Example:
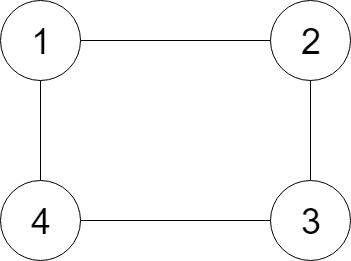
Input:
{"$id":"1","neighbors":[{"$id":"2","neighbors":[{"$ref":"1"},{"$id":"3","neighbors":[{"$ref":"2"},{"$id":"4","neighbors":[{"$ref":"3"},{"$ref":"1"}],"val":4}],"val":3}],"val":2},{"$ref":"4"}],"val":1}
Explanation:
Node 1's value is 1, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 2's value is 2, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Node 3's value is 3, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 4's value is 4, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Note:
- The number of nodes will be between 1 and 100.
- The undirected graph is a simple graph, which means no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- Since the graph is undirected, if node p has node q as neighbor, then node q must have node p as neighbor too.
- You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Solutions:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> neighbors;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> oldToNew;
return helper(node, oldToNew);
}
Node* helper(Node* node, unordered_map<Node*, Node*>& oldToNew) {
if (node == NULL) return NULL;
if (oldToNew.count(node) > 0) return oldToNew[node];
Node* newNode = new Node(node->val, {});
oldToNew[node] = newNode;
for (auto& neighbor : node->neighbors) {
newNode->neighbors.push_back(helper(neighbor, oldToNew));
}
return newNode;
}
};